Jdbc与连接池
Author: Gentleman.Hu
Create Time: 2020-10-03 15:28:51
Modified by: Gentleman.Hu
Modified time: 2020-10-07 16:11:55
Email: [email protected]
Home: https://crushing.xyz
Description:JDBC与连接池
QuickGuide Java DataBase COnnectivity
JDBC与基本CRUD
基本
基本步骤
注册驱动
建立连接
获取数据库连接对象(Connection)
定义sql语句
获取sql执行对象(Statement)
执行sql,获取结果
处理结果
关闭连接,释放资源
OnAction 1. 引入包
import java.sql.*;2. 注册驱动Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver)3. 建立连接static final String USER = "username"; static final String PASS = "password"; System.out.println("Connecting to database...); conn = DriverManager.getConnection(DB_URL,USER,PASS);执行sql
System.out.println("Creating statement ...); stmt = conn.createStatement(); String sql; sql = "select * from one_table"; ResultSet rs = stmt.executeQuery(sql);处理结果
while(rs.next()){ int id = rs.getInt("id"); int age = rs.getInt("age"); String first = rs.getString("first"); String last = rs.getString("last"); //Display values System.out.print("ID: " + id); System.out.print(", Age: " + age); System.out.print(", First: " + first); System.out.println(", Last: " + last); }关闭连接,释放资源
rs.close(); stmt.close(); conn.close();
Full
相关Exception表一览
Method
Description
getErrorCode( )
Gets the error number associated with the exception.
getMessage( )
Gets the JDBC driver's error message for an error handled by the driver or gets the Oracle error number and message for a database error.
getSQLState( )
Gets the XOPEN SQLstate string. For a JDBC driver error, no useful information is returned from this method. For a database error, the five-digit XOPEN SQLstate code is returned. This method can return null.
getNextException( )
Gets the next Exception object in the exception chain.
printStackTrace( )
Prints the current exception, or throwable, and its backtrace to a standard error stream.
printStackTrace(PrintStream s)
Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the print stream you specify.
printStackTrace(PrintWriter w)
Prints this throwable and its backtrace to the print writer you specify.
用try catch finally包裹
JDBC 中Data 类型对应表
SQL
JDBC/Java
setXXX
updateXXX
VARCHAR
java.lang.String
setString
updateString
CHAR
java.lang.String
setString
updateString
LONGVARCHAR
java.lang.String
setString
updateString
BIT
boolean
setBoolean
updateBoolean
NUMERIC
java.math.BigDecimal
setBigDecimal
updateBigDecimal
TINYINT
byte
setByte
updateByte
SMALLINT
short
setShort
updateShort
INTEGER
int
setInt
updateInt
BIGINT
long
setLong
updateLong
REAL
float
setFloat
updateFloat
FLOAT
float
setFloat
updateFloat
DOUBLE
double
setDouble
updateDouble
VARBINARY
byte[ ]
setBytes
updateBytes
BINARY
byte[ ]
setBytes
updateBytes
DATE
java.sql.Date
setDate
updateDate
TIME
java.sql.Time
setTime
updateTime
TIMESTAMP
java.sql.Timestamp
setTimestamp
updateTimestamp
CLOB
java.sql.Clob
setClob
updateClob
BLOB
java.sql.Blob
setBlob
updateBlob
ARRAY
java.sql.Array
setARRAY
updateARRAY
REF
java.sql.Ref
SetRef
updateRef
STRUCT
java.sql.Struct
SetStruct
updateStruct
批处理 JDBC - Batch Processing
Batch Processing allows you to group related SQL statements into a batch and submit them with one call to the database.
When you send several SQL statements to the database at once, you reduce the amount of communication overhead, thereby improving performance.
JDBC drivers are not required to support this feature. You should use the DatabaseMetaData.supportsBatchUpdates() method to determine if the target database supports batch update processing. The method returns true if your JDBC driver supports this feature.
The addBatch() method of Statement, PreparedStatement, and CallableStatement is used to add individual statements to the batch. The executeBatch() is used to start the execution of all the statements grouped together.
The executeBatch() returns an array of integers, and each element of the array represents the update count for the respective update statement.
Just as you can add statements to a batch for processing, you can remove them with the clearBatch() method. This method removes all the statements you added with the addBatch() method. However, you cannot selectively choose which statement to remove.
Streaming Data(流):
A PreparedStatement object has the ability to use input and output streams to supply parameter data. This enables you to place entire files into database columns that can hold large values, such as CLOB and BLOB data types.
There are following methods which can be used to stream data:
setAsciiStream(): This method is used to supply large ASCII values.
setCharacterStream(): This method is used to supply large UNICODE values.
setBinaryStream(): This method is used to supply large binary values.
The setXXXStream() method requires an extra parameter, the file size, besides the parameter placeholder. This parameter informs the driver how much data should be sent to the database using the stream.
事务
事务:一个包含多个步骤的业务操作。如果这个业务操作被事务管理,则这多个步骤要么同时成功,要么同时失败。
使用Connection对象来管理事务
开启事务:setAutoCommit(boolean autoCommit) :调用该方法设置参数为false,即开启事务
在执行sql之前开启事务
提交事务:commit()
当所有sql都执行完提交事务
回滚事务:rollback()
在catch中回滚事务
简单demo
数据库连接池与JDBC Template
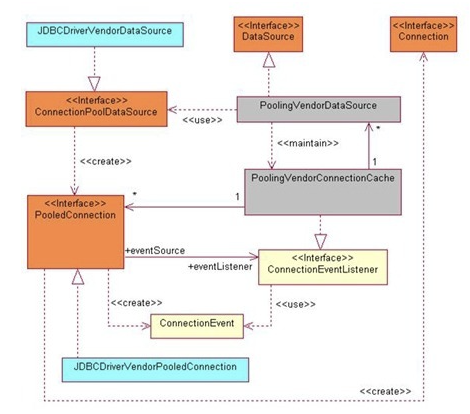
基础连接池
一个容器(集合),存放数据库连接的容器。 当系统初始化好后,容器被创建,容器中会申请一些连接对象,当用户来访问数据库时,从容器中获取连接对象,用户访问完之后,会将连接对象归还给容器。
好处: 1. 节约资源 2. 用户访问高效
实现: 标准接口:DataSource javax.sql包下的
方法:
获取连接:getConnection()
归还连接:Connection.close()。如果连接对象Connection是从连接池中获取的,那么调用Connection.close()方法,则不会再关闭连接了。而是释放连接
几个常见厂商实现的数据库连接池 1. C3P0:数据库连接池技术 2. Druid:数据库连接池实现技术,由阿里巴巴提供的
c3p0配置文件
c3p0.properties或者c3p0-config.xml直接放置在
src目录即可
c3p0创建过程
ComboPooledDataSource
getConnection
Druid:
配置文件
可以properties
可以任意名称,任意位置
过程
加载配置文件.Properties
通过工厂获取连接池对象.
DruidDataSourceFactory获取连接:
getConnection
Full in util class
Spring JDBC
Spring JDBCTemplate class method table
No.
Method
Description
1)
public int update(String query)
is used to insert, update and delete records.
2)
public int update(String query,Object... args)
is used to insert, update and delete records using PreparedStatement using given arguments.
3)
public void execute(String query)
is used to execute DDL query.
4)
public T execute(String sql, PreparedStatementCallback action)
executes the query by using PreparedStatement callback.
5)
public T query(String sql, ResultSetExtractor rse)
is used to fetch records using ResultSetExtractor.
6)
public List query(String sql, RowMapper rse)
is used to fetch records using RowMapper.
Employee.java
EmployeeDao.java
applicationContext.xml
Test.java
Another(Not written by Gentleman.Hu)
Spring框架对JDBC的简单封装。提供了一个JDBCTemplate对象简化JDBC的开发
步骤:
导入jar包
创建JdbcTemplate对象。依赖于数据源DataSource
JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(ds);
调用JdbcTemplate的方法来完成CRUD的操作
update():执行DML语句。增、删、改语句
queryForMap():查询结果将结果集封装为map集合,将列名作为key,将值作为value 将这条记录封装为一个map集合
注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1
queryForList():查询结果将结果集封装为list集合
注意:将每一条记录封装为一个Map集合,再将Map集合装载到List集合中
query():查询结果,将结果封装为JavaBean对象
query的参数:RowMapper
一般我们使用BeanPropertyRowMapper实现类。可以完成数据到JavaBean的自动封装
new BeanPropertyRowMapper<类型>(类型.class)
queryForObject:查询结果,将结果封装为对象
一般用于聚合函数的查询
练习:
需求: 1. 修改1号数据的 salary 为 10000 2. 添加一条记录 3. 删除刚才添加的记录 4. 查询id为1的记录,将其封装为Map集合 5. 查询所有记录,将其封装为List 6. 查询所有记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合 7. 查询总记录数
代码:
```java import cn.itcast.domain.Emp; import cn.itcast.utils.JDBCUtils; import org.junit.Test; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.BeanPropertyRowMapper; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate; import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import java.sql.Date; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; import java.util.Map;
public class JdbcTemplateDemo2 {
//1. 获取JDBCTemplate对象 private JdbcTemplate template = new JdbcTemplate(JDBCUtils.getDataSource()); /**
修改1号数据的 salary 为 10000
*/
@Test
public void test1(){
//2. 定义sql String sql = "update emp set salary = 10000 where id = 1001"; //3. 执行sql int count = template.update(sql); System.out.println(count); }
/**
添加一条记录
*/
@Test
public void test2(){
String sql = "insert into emp(id,ename,dept_id) values(?,?,?)";
int count = template.update(sql, 1015, "郭靖", 10);
System.out.println(count);
}
/**
3.删除刚才添加的记录 */ @Test public void test3(){ String sql = "delete from emp where id = ?"; int count = template.update(sql, 1015); System.out.println(count); }
/**
4.查询id为1001的记录,将其封装为Map集合
注意:这个方法查询的结果集长度只能是1 / @Test public void test4(){ String sql = "select from emp where id = ? or id = ?"; Map map = template.queryForMap(sql, 1001,1002); System.out.println(map); //{id=1001, ename=孙悟空, job_id=4, mgr=1004, joindate=2000-12-17, salary=10000.00, bonus=null, dept_id=20}
}
/**
查询所有记录,将其封装为List
*/
@Test
public void test5(){
String sql = "select * from emp";
List> list = template.queryForList(sql);
for (Map stringObjectMap : list) { System.out.println(stringObjectMap); } }
/**
查询所有记录,将其封装为Emp对象的List集合
*/
@Test public void test6(){ String sql = "select * from emp"; List list = template.query(sql, new RowMapper() {
});
for (Emp emp : list) { System.out.println(emp); } }
} ```
Last updated